List of first 50 elements of the periodic table by atomic number including the chemical symbol and the atomic weight. You can print the list of elements by hitting the print button below.
| Atomic Number | Chemical Symbol | Element Name | Atomic Weight (u) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | Hydrogen | 1.008 |
| 2 | He | Helium | 4.002602 |
| 3 | Li | Lithium | 6.94 |
| 4 | Be | Beryllium | 9.0121831 |
| 5 | B | Boron | 10.81 |
| 6 | C | Carbon | 12.011 |
| 7 | N | Nitrogen | 14.007 |
| 8 | O | Oxygen | 15.999 |
| 9 | F | Fluorine | 18.99840316 |
| 10 | Ne | Neon | 20.1797 |
| 11 | Na | Sodium | 22.98976928 |
| 12 | Mg | Magnesium | 24.305 |
| 13 | Al | Aluminium | 26.9815385 |
| 14 | Si | Silicon | 28.085 |
| 15 | P | Phosphorus | 30.973762 |
| 16 | S | Sulfur | 32.06 |
| 17 | Cl | Chlorine | 35.45 |
| 18 | Ar | Argon | 39.948 |
| 19 | K | Potassium | 39.0983 |
| 20 | Ca | Calcium | 40.078 |
| 21 | Sc | Scandium | 44.955908 |
| 22 | Ti | Titanium | 47.867 |
| 23 | V | Vanadium | 50.9415 |
| 24 | Cr | Chromium | 51.9961 |
| 25 | Mn | Manganese | 54.938044 |
| 26 | Fe | Iron | 55.845 |
| 27 | Co | Cobalt | 58.933194 |
| 28 | Ni | Nickel | 58.6934 |
| 29 | Cu | Copper | 63.546 |
| 30 | Zn | Zinc | 65.38 |
| 31 | Ga | Gallium | 69.723 |
| 32 | Ge | Germanium | 72.63 |
| 33 | As | Arsenic | 74.921595 |
| 34 | Se | Selenium | 78.971 |
| 35 | Br | Bromine | 79.904 |
| 36 | Kr | Krypton | 83.798 |
| 37 | Rb | Rubidium | 85.4678 |
| 38 | Sr | Strontium | 87.62 |
| 39 | Y | Yttrium | 88.90584 |
| 40 | Zr | Zirconium | 91.224 |
| 41 | Nb | Niobium | 92.90637 |
| 42 | Mo | Molybdenum | 95.95 |
| 43 | Tc | Technetium | 98 |
| 44 | Ru | Ruthenium | 101.07 |
| 45 | Rh | Rhodium | 102.9055 |
| 46 | Pd | Palladium | 106.42 |
| 47 | Ag | Silver | 107.8682 |
| 48 | Cd | Cadmium | 112.414 |
| 49 | In | Indium | 114.818 |
| 50 | Sn | Tin | 118.71 |
The atomic number of a sodium atom is 11 and its mass number is 23. Calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons it contains. Number of protons = 11. So the atomic number is symbolized by Z and it refers to the number of protons in a nucleus and you can find the atomic number on the periodic table so we're going to talk about hydrogen in this video so for hydrogen hydrogen's atomic number is 1 so it's right here so there's one proton in the nucleus of a hydrogen atom in a neutral atom the number of protons is equal to the number of. Define atomic number. Atomic number synonyms, atomic number pronunciation, atomic number translation, English dictionary definition of atomic number. The atomic number (represented by the letter Z) of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element.An atom can be classified as a particular element based solely on its atomic number. For example, any atom with an atomic number of 8 (its nucleus contains 8 protons) is an oxygen atom, and any atom with a different number of protons would be a. Chemical elements listed by atomic number The elements of the periodic table sorted by atomic number. Click on any elements name for further chemical properties, environmental data or health effects. This list contains the 118 elements of chemistry.

Learning Objective
- Determine the relationship between the mass number of an atom, its atomic number, its atomic mass, and its number of subatomic particles
Key Points
- Neutral atoms of each element contain an equal number of protons and electrons.
- The number of protons determines an element’s atomic number and is used to distinguish one element from another.
- The number of neutrons is variable, resulting in isotopes, which are different forms of the same atom that vary only in the number of neutrons they possess.
- Together, the number of protons and the number of neutrons determine an element’s mass number.
- Since an element’s isotopes have slightly different mass numbers, the atomic mass is calculated by obtaining the mean of the mass numbers for its isotopes.
Terms
Atomic Number Pr
- atomic massThe average mass of an atom, taking into account all its naturally occurring isotopes.
- mass numberThe sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in an atom.
- atomic numberThe number of protons in an atom.
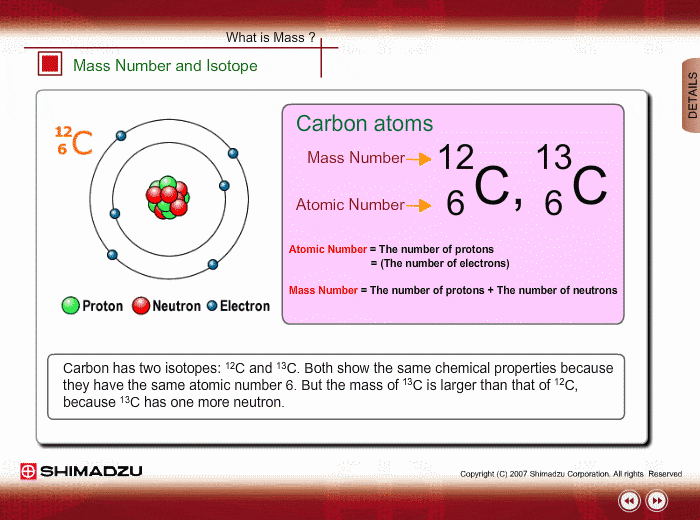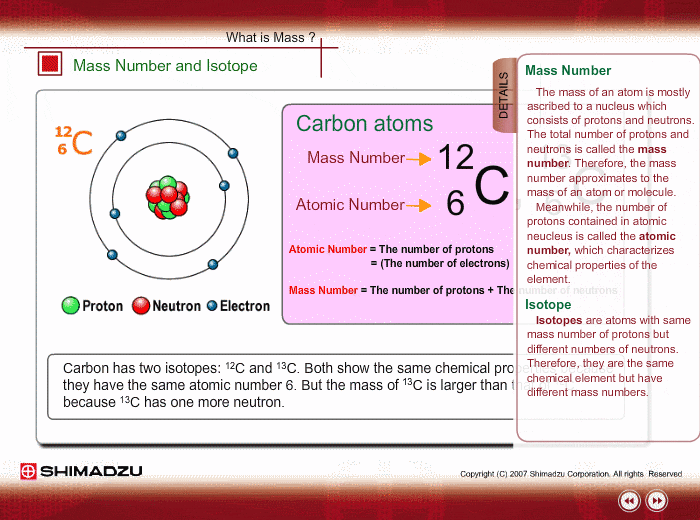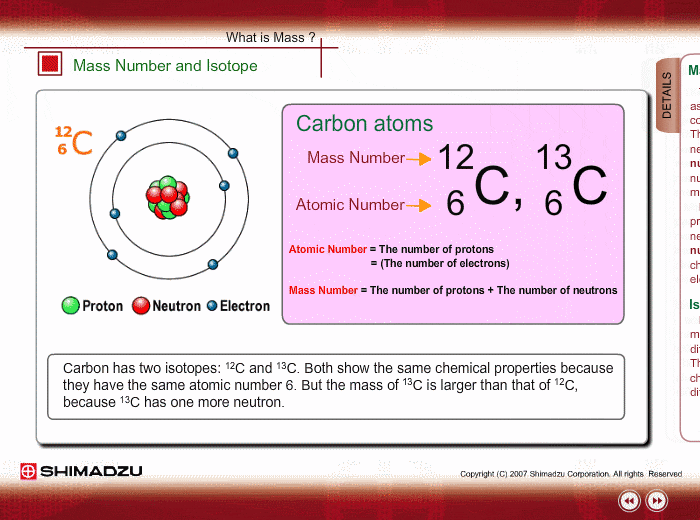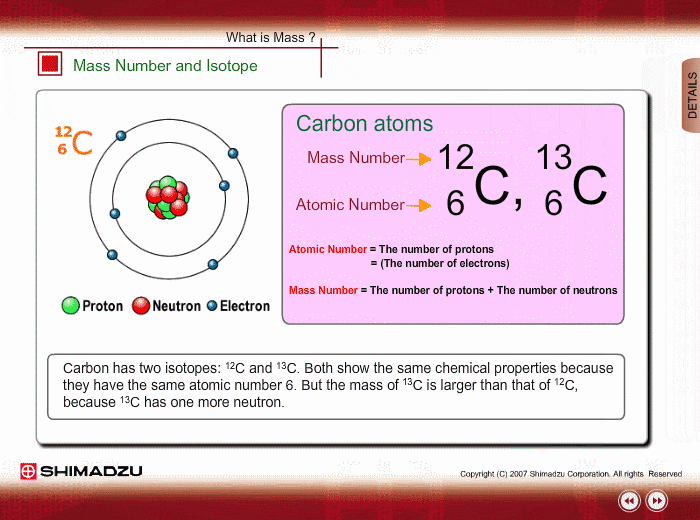
Atomic Number
Neutral atoms of an element contain an equal number of protons and electrons. The number of protons determines an element’s atomic number (Z) and distinguishes one element from another. For example, carbon’s atomic number (Z) is 6 because it has 6 protons. The number of neutrons can vary to produce isotopes, which are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The number of electrons can also be different in atoms of the same element, thus producing ions (charged atoms). For instance, iron, Fe, can exist in its neutral state, or in the +2 and +3 ionic states.
Mass Number
An element’s mass number (A) is the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons. The small contribution of mass from electrons is disregarded in calculating the mass number. This approximation of mass can be used to easily calculate how many neutrons an element has by simply subtracting the number of protons from the mass number. Protons and neutrons both weigh about one atomic mass unit or amu. Isotopes of the same element will have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
Scientists determine the atomic mass by calculating the mean of the mass numbers for its naturally-occurring isotopes. Often, the resulting number contains a decimal. For example, the atomic mass of chlorine (Cl) is 35.45 amu because chlorine is composed of several isotopes, some (the majority) with an atomic mass of 35 amu (17 protons and 18 neutrons) and some with an atomic mass of 37 amu (17 protons and 20 neutrons).
Atomic Number Of 2
Given an atomic number (Z) and mass number (A), you can find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in a neutral atom. For example, a lithium atom (Z=3, A=7 amu) contains three protons (found from Z), three electrons (as the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in an atom), and four neutrons (7 – 3 = 4).
The Atomic Number Of An Element Is
Show SourcesBoundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
http://www.boundless.com/
Boundless Learning
CC BY-SA 3.0.
http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/atomic_number
Wiktionary
CC BY-SA 3.0.
http://www.boundless.com//biology/definition/atomic-mass–2
Boundless Learning
CC BY-SA 3.0.

http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/A-level_Chemistry/OCR/Atoms,_Bonds_and_Groups/Atoms_and_Reactions/Atoms
Wikibooks
CC BY-SA 3.0.
http://cnx.org/content/m44390/latest/?collection=col11448/latest
OpenStax CNX
CC BY 3.0.
